nur für Forschungszwecke
SRT1720 HCl Sirtuin Aktivator
Kat.-Nr.S1129
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 506.02
Qualitätskontrolle
Produkte, die oft zusammen verwendet werden mit SRT1720 HCl
| Verwandte Ziele | HDAC JAK BET Histone Methyltransferase PKC PARP HIF PRMT EZH2 AMPK |
|---|---|
| Weitere Sirtuin Inhibitoren | Sirtinol Fisetin 3-TYP AGK2 SRT2104 (GSK2245840) OSS_128167 SirReal2 Thiomyristoyl NRD167 SRT2183 |
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CACs | Function Assay | 4 μM | 30 min | DMSO | induces acute SIRT1 activation | 26254104 |
| MC3T3-E1 | Function Assay | 10 µM | 1 h | reduces the TGF-β-stimulated VEGF release in dose- and time-dependent manner | 26136978 | |
| MC3T3-E1 | Function Assay | 10 µM | 12 h | reduces the VEGF mRNA expression levels stimulated by TGF-β | 26136978 | |
| MC3T3-E1 | Function Assay | 20 μM | 1 h | suppresses the TGF-β-induced phosphorylation of p44/p42 MAP kinase or SAPK/JNK | 26136978 | |
| WE-68 | Apoptosis Assay | 0-24 μM | 24 h | induces cell death in dose dependently | 26055805 | |
| SK-ES-1 | Apoptosis Assay | 0-10 μM | 24 h | induces cell death in dose dependently | 26055805 | |
| SK-N-MC | Apoptosis Assay | 0-2.5 μM | 24 h | induces cell death in dose dependently | 26055805 | |
| WE-68 | Function Assay | 20 μM | 0-24 h | activates caspase 3/7 | 26055805 | |
| SK-ES-1 | Function Assay | 10 μM | 0-24 h | activates caspase 3/7 | 26055805 | |
| SK-N-MC | Function Assay | 3 μM | 0-24 h | activates caspase 3/7 | 26055805 | |
| NRK-49F | Function Assay | 0–2 μM | 36 h | increases expression of α-SMA and fibronectin dose dependently | 26022003 | |
| NRK-49F | Function Assay | 0–2 μM | 36 h | enhances phosphorylation of EGFR and PDGFRβ | 26022003 | |
| NRK-49F | Function Assay | 0–2 μM | 36 h | enhances STAT3 phosphorylation | 26022003 | |
| RAW264.7 | Function Assay | 1 μM | 6 h | upregulates the reduced SIRT1 protein or mRNA levels by high glucose | 25793995 | |
| MCF10A | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-20 μM | 24 h | reduces cell viability dose dependently | 25411356 | |
| MCF-7 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-20 μM | 24 h | reduces cell viability dose dependently | 25411356 | |
| T47D | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-20 μM | 24 h | reduces cell viability dose dependently | 25411356 | |
| SKBR3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-20 μM | 24 h | reduces cell viability dose dependently | 25411356 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-20 μM | 24 h | reduces cell viability dose dependently | 25411356 | |
| SUM149 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-20 μM | 24 h | reduces cell viability dose dependently | 25411356 | |
| HS578T | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-20 μM | 24 h | reduces cell viability dose dependently | 25411356 | |
| BT20 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-20 μM | 24 h | reduces cell viability dose dependently | 25411356 | |
| A459 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-20 μM | 24 h | reduces cell viability dose dependently | 25411356 | |
| HCT116 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-20 μM | 24 h | reduces cell viability dose dependently | 25411356 | |
| Neu | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-20 μM | 24 h | reduces cell viability dose dependently | 25411356 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Function Assay | 5 μM | 8 h | increases the number of acidic vesicular organelles | 25411356 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Function Assay | 5 μM | 16 h | induces lysosomal membrane permeabilization | 25411356 | |
| MC3T3-E1 | Function Assay | 10 μM | 60 min | suppresses the FGF-2-stimulated osteoprotegerin release | 25290095 | |
| MC3T3-E1 | Function Assay | 10 μM | 60 min | attenuates the FGF-2-induced osteoprotegerin mRNA expression | 25290095 | |
| MC3T3-E1 | Function Assay | 10 μM | 60 min | attenuates the FGF-2-induced osteoprotegerin mRNA expression | 25290095 | |
| MC3T3-E1 | Function Assay | 10 μM | 60 min | suppresses the BMP-4-stimulated VEGF release | 24435444 | |
| MC3T3-E1 | Function Assay | 10 μM | 60 min | suppresses the PGF2α-stimulated OPG release | 24333336 | |
| MC3T3-E1 | Function Assay | 10 μM | 60 min | reduces the PGF2α-stimulated phosphorylation of p44/p42 MAP kinase | 24333336 | |
| MC3T3-E1 | Function Assay | 10 μM | 60 min | attenuates the PGF2α-induced phosphorylation of both MEK1/2 and Raf-1 | 24333336 | |
| RPE | Cell Viability Assay | 5 µM | 1 h | attenuates OAβ-induced decrease of cell viability | 24036938 | |
| 9607 | Cell Viability Assay | 1 μM | 36 h | increases the cell viability compared with melatonin alone | 23726949 | |
| 9607 | Function Assay | 1 μM | 36 h | increases SIRT1 and decreased acetylated-p53 expression | 23726949 | |
| RPMI.8226 | Cell Viability Assay | 7/10 μM | 24 h | decreases viability concentration dependently | 21950728 | |
| U266 | Cell Viability Assay | 7/10 μM | 24 h | decreases viability concentration dependently | 21950728 | |
| MM.1S | Cell Viability Assay | 7/10 μM | 24 h | decreases viability concentration dependently | 21950728 | |
| KMS12 | Cell Viability Assay | 7/10 μM | 24 h | decreases viability concentration dependently | 21950728 | |
| LR5 | Cell Viability Assay | 7/10 μM | 24 h | decreases viability concentration dependently | 21950728 | |
| MM.1R | Cell Viability Assay | 7/10 μM | 24 h | decreases viability concentration dependently | 21950728 | |
| Ina6 | Cell Viability Assay | 7/10 μM | 24 h | decreases viability concentration dependently | 21950728 | |
| RPMI-8226 | Apoptosis Assay | 7/10 μM | 24 h | induces a significant increase in the Annexin V+/PI− apoptosis | 21950728 | |
| MM.1R | Apoptosis Assay | 7/10 μM | 24 h | induces a significant increase in the Annexin V+/PI− apoptosis | 21950728 | |
| H411EC3 | Function Assay | 50/100 nM | 6 h | increases SIRT1 activity in the presence of TSA, PEPCK activity, mRNA levels of Pck1 and Pgc1α, and elevating glucose production | 21212096 | |
| hepatocytes | Function Assay | 10 nM | 6 h | increases SIRT1 activity in the presence of TSA, PEPCK activity, mRNA levels of Pck1 and Pgc1α, and elevating glucose production | 21212096 | |
| hepatocytes | Function Assay | 10 nM | 6 h | increases Hmgcr and Acc gene expression | 21212096 | |
| U2OS | Function assay | 0.10 uM | Activation of SIRT1 in human U2OS cells assessed as decrease in p53 deacetylation level at 0.10 uM | 18046409 | ||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh30 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh30 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 506.02 | Formel | C25H23N7OS.HCl |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 1001645-58-4 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | N/A | Smiles | C1CN(CCN1)CC2=CSC3=NC(=CN23)C4=CC=CC=C4NC(=O)C5=NC6=CC=CC=C6N=C5.Cl | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 100 mg/mL
(197.62 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
SIRT1
(Cell-free assay) 0.16 μM(EC50)
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Das maximale Aktivierungsverhältnis von SRT1720 im Vergleich zu den nächsten Sirtuin-Homologen, SIRT2 (EC1.5 = 37 μM) und SIRT3 (EC1.5 > 300 μM), beträgt bis zu 781 %. SRT1720 bindet an den SIRT1-Enzym-Peptid-Substratkomplex an einer allosterischen Stelle amino-terminal zur katalytischen Domäne und senkt die Michaelis-Konstante für acetylierte Substrate. SRT1720 könnte die Glukosespiegel im gefütterten Zustand senken. SRT1720 hat keinen Einfluss auf den Nüchternglukosespiegel bei Mäusen, die mit Standardfutter gefüttert wurden, was darauf hindeutet, dass eine pharmakologische SIRT1-Aktivierung unwahrscheinlich ist, eine Hypoglykämie zu induzieren. SRT1720 reduziert die Hyperinsulinämie nach 4 Wochen signifikant und normalisiert teilweise erhöhte Insulinspiegel. Die SRT1720-Behandlung erhöht die mitochondriale Kapazität im Gastrocnemius-Muskel um 15 %, gemessen an der Citratsynthase-Aktivität. Höhere Konzentrationen von SRT1720 (15 μM) induzieren eine leichte (10-20 %) Abnahme der Viabilität normaler Zellen. SRT1720 hemmt auch signifikant die VEGF-abhängige MM-Zellmigration. |
| Kinase-Assay |
SIRT1-Fluoreszenzpolarisationsassay
|
|
Im SIRT1-FP-Assay wird die SIRT1-Aktivität unter Verwendung eines 20 Aminosäuren umfassenden Peptids (Ac-Glu-Glu-Lys(Biotin)-Gly-Gln-Ser-Thr-Ser-Ser-His-Ser-Lys(Ac)-Nle-Ser-Thr-Glu-Gly–Lys(MR121 oder Tamra)-Glu-Glu-NH2) überwacht, das aus der Sequenz von p53 abgeleitet ist. Das Peptid ist N-terminal mit Biotin verknüpft und C-terminal mit einem Fluoreszenz-Tag modifiziert. Die Reaktion zur Überwachung der Enzymaktivität ist ein gekoppelter Enzymassay, wobei die erste Reaktion die von SIRT1 katalysierte Deacetylierungsreaktion ist und die zweite Reaktion die Spaltung durch Trypsin an dem neu exponierten Lysinrest ist. Die Reaktion wird gestoppt und Streptavidin wird hinzugefügt, um die Massenunterschiede zwischen Substrat und Produkt zu betonen. Die Empfindlichkeit des FP-Assays ermöglicht die Identifizierung von SRT1720. Die Reaktionsbedingungen der Fluoreszenzpolarisation sind wie folgt: 0,5 μM Peptidsubstrat, 150 μM βNAD+, 0-10 nM SIRT1, 25 mM Tris-Acetat pH 8, 137 mM Na-Ac, 2,7 mM K-Ac, 1 mM Mg-Ac, 0,05 % Tween-20, 0,1 % Pluronic F127, 10 mM CaCl 2, 5 mM DTT, 0,025 % BSA und 0,15 mM Nicotinamid. Die Reaktion wird bei 37 °C inkubiert und durch Zugabe von Nicotinamid gestoppt, und Trypsin wird hinzugefügt, um das deacetylierte Substrat zu spalten. Diese Reaktion wird bei 37 °C in Gegenwart von 1 μM Streptavidin inkubiert. Die Fluoreszenzpolarisation wird bei Anregungs-(650 nm) und Emissions-(680 nm) Wellenlängen bestimmt.
|
|
| In vivo |
Bei DIO-Mäusen imitiert SRT1720 mehrere der nach Kalorienrestriktion beobachteten Effekte, einschließlich verbesserter Insulinsensitivität, normalisierter Glukose- und Insulinspiegel und erhöhter mitochondrialer Kapazität. Zusätzlich verbessert SRT1720 bei diätinduziert fettleibigen und genetisch fettleibigen Mäusen die Insulinsensitivität, senkt den Plasmaglukosespiegel und erhöht die mitochondriale Kapazität. Somit ist SRT1720 ein vielversprechendes neues Therapeutikum zur Behandlung von altersbedingten Krankheiten wie Typ-2-Diabetes. Im Einklang mit einer verbesserten Glukosetoleranz ist die Glukoseinfusionsrate, die zur Aufrechterhaltung der Euglykämie erforderlich ist, bei SRT1720-behandelten fa/fa-Ratten etwa 35 % höher, und die Gesamtglukoseentsorgungsrate ist um etwa 20 % erhöht. SRT1720 verhindert auch das Wachstum von Multiples Myelom-Tumoren. |
Literatur |
|
Anwendungen
| Methoden | Biomarker | Bilder | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | Cleaved-PARP-1 / Cleaved-caspase-3 / LC3-II / p62 / SIRT1 |
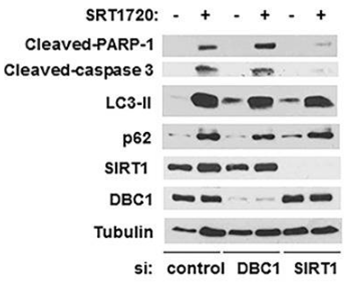
|
26655844 |
| Immunofluorescence | Cathepsin B |
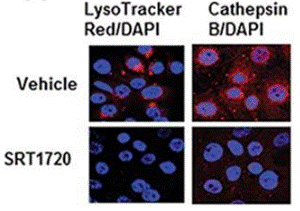
|
26655844 |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |

|
25411356 |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Frage 1:
How can we prepare it for in vivo mouse studies?
Antwort:
It can be dissolved in 30% PEG 400+0.5% Tween 80+5% Propylene glycol at 30mg/ml as a suspension, which is fine for oral gavage. We’ve also found that it can be dissolved in 2% DMSO+30% PEG 300+1% Tween 80+ddH2O at 3mg/ml clearly, making it suitable for injection. When preparing the solution, please dissolve the compound in DMSO clearly first, then add PEG and Tween. After they are mixed well, dilute with water.
